GERD/Hiatus Hernia
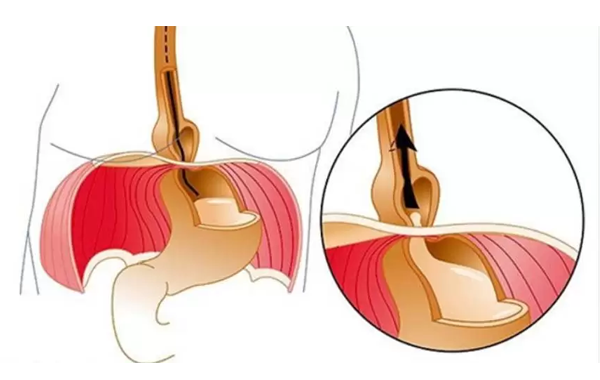
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and hiatus hernia are related conditions that affect the digestive system, particularly the esophagus and stomach. Here’s an overview of both, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
GERD is a chronic condition where stomach acid or, occasionally, bile flows back into the esophagus, leading to irritation.
Symptoms
- Heartburn (burning sensation in the chest)
- Regurgitation of food or sour liquid
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Chest pain
- Chronic cough or throat clearing
- Hoarseness or sore throat
- Feeling of a lump in the throat
- Nausea
Hiatus Hernia
A hiatus hernia occurs when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, which can contribute to GERD symptoms.
Symptoms:
- Similar to GERD symptoms (heartburn, regurgitation)
- Pain or discomfort in the chest or upper abdomen
- Difficulty swallowing
- Shortness of breath (in severe cases)
Causes
GERD:
- Weak lower esophageal sphincter (LES)
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Smoking
- Certain medications (e.g., antihistamines, painkillers)
- Diet (fatty foods, spicy foods, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol)
Hiatus Hernia:
- Congenital (present at birth)
- Age-related changes (weakening of the diaphragm)
- Increased pressure in the abdomen (from obesity, pregnancy, heavy lifting, or persistent coughing)




